Digital Health Technologies: Telehealth Solutions and Remote Care
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving world, Digital Health Technologies are revolutionizing how we approach healthcare. With rising healthcare costs and the need for efficient, accessible care, telehealth solutions and remote care have become critical components of modern medical practice. As a result, understanding the potential of Digital Health Technologies is essential not only for healthcare providers but also for patients and policy makers. In this article, we explore the transformative impact of telehealth, discuss its benefits and challenges, and offer actionable strategies for embracing remote care. If you’re ready to learn how Digital Health Technologies are shaping the future of healthcare, let’s dive in.
For more digital transformation insights, visit our Digital Health Technologies section at TechWorldTrends.com.
1. Overview of Digital Health Technologies
1.1 What Are Digital Health Technologies?
Digital Health Technologies refer to the integration of digital tools and advanced technology into healthcare services. These technologies include telehealth solutions, wearable devices, electronic health records, and mobile health apps. They are designed to improve the delivery, efficiency, and accessibility of healthcare services while reducing costs and improving patient outcomes.
Moreover, the advent of remote care has expanded the reach of healthcare, enabling patients to consult with providers via video calls, chatbots, and remote monitoring systems. In addition, digital health solutions foster better data management and real-time communication, which are essential for personalized care.
1.2 The Growth of Telehealth
Telehealth has experienced exponential growth in recent years, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. This surge is due to the necessity for social distancing and the convenience of receiving care without physically visiting a healthcare facility. Today, telehealth solutions are a cornerstone of Digital Health Technologies and continue to evolve with advancements in technology.
Furthermore, governments and private sectors alike are investing heavily in telehealth infrastructure, recognizing its potential to transform healthcare delivery on a global scale.
2. Telehealth Solutions: What They Are and How They Work
2.1 Understanding Telehealth
Telehealth is the use of digital information and communication technologies to access healthcare services remotely. It encompasses various methods such as video consultations, remote patient monitoring, and mobile health applications. Essentially, telehealth bridges the gap between patients and healthcare providers, making care more accessible and efficient.
In addition, telehealth platforms often include features like electronic prescriptions, appointment scheduling, and secure messaging, all of which contribute to a seamless healthcare experience.
For more telehealth information
2.2 Key Components of Telehealth Solutions
Successful telehealth solutions integrate multiple components that work together to provide comprehensive remote care. These components include:
- Video Conferencing: Secure, high-quality video communication between patients and healthcare providers.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: Devices and sensors that collect health data in real-time and transmit it to healthcare professionals.
- Mobile Health Apps: Applications that allow patients to track their health, schedule appointments, and receive health tips on the go.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Digital storage of patient records for easy access and sharing between providers.
Furthermore, integrating these components creates an ecosystem where healthcare is more personalized, efficient, and accessible.
3. The Benefits of Telehealth and Remote Care
3.1 Enhancing Accessibility and Convenience
One of the primary benefits of Digital Health Technologies is the enhanced accessibility they offer. Telehealth enables patients, especially those in remote or underserved areas, to access high-quality care without the need for travel. This convenience is particularly valuable for patients with chronic conditions who require regular monitoring and consultations.
Moreover, telehealth reduces the burden on healthcare facilities by managing non-emergency consultations online, allowing hospitals and clinics to focus on critical cases.
3.2 Reducing Healthcare Costs
Remote care solutions can significantly lower healthcare costs for both providers and patients. By eliminating the need for physical appointments, telehealth minimizes overhead expenses and reduces travel-related costs. This economic advantage makes healthcare more affordable and sustainable.
Additionally, improved efficiency through Digital Health Technologies leads to quicker diagnosis and treatment, ultimately saving time and resources.
3.3 Improving Patient Outcomes and Engagement
Telehealth solutions enhance patient outcomes by enabling continuous monitoring and timely intervention. Patients are more engaged in their healthcare when they have convenient access to care and real-time feedback from providers. This ongoing engagement fosters better adherence to treatment plans and healthier lifestyles.
Furthermore, digital tools empower patients by providing them with personalized health insights, leading to a proactive approach to managing their well-being.
4. Challenges and Considerations in Remote Care
4.1 Technical and Infrastructure Challenges
Despite its numerous benefits, implementing telehealth comes with challenges. Technical issues such as poor internet connectivity, device compatibility, and data security are common concerns. Ensuring robust infrastructure and reliable digital health platforms is critical for the success of remote care.
In addition, healthcare providers must invest in secure platforms that comply with regulatory standards to protect patient data.
4.2 Regulatory and Privacy Concerns
Regulatory compliance and patient privacy are significant challenges in telehealth. With the increasing amount of sensitive health data being transmitted digitally, maintaining strict data protection and privacy standards is essential. Healthcare providers need to adhere to laws such as HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in Europe to ensure patient trust.
Moreover, clear policies and guidelines must be established to govern the use of telehealth technologies, ensuring that both providers and patients are well-protected.
4.3 Patient and Provider Adoption
While telehealth offers many advantages, its adoption by both patients and healthcare providers can be slow. Some patients may be reluctant to use digital platforms due to concerns about technology or privacy, while providers may face challenges in integrating telehealth into their existing workflows.
Furthermore, ongoing training and support are essential to ensure that all stakeholders are comfortable with using Digital Health Technologies effectively.
5. Future Trends and Innovations in Digital Health Technologies
5.1 Integration of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is set to further revolutionize the telehealth industry. AI-powered tools can analyze patient data in real time, provide predictive insights, and even automate routine tasks. This integration will enhance the efficiency of telehealth services and improve patient outcomes.
Moreover, machine learning algorithms can personalize patient care by tailoring treatment plans based on individual health data. These advancements will make remote care more adaptive and responsive to patient needs.
5.2 Expansion of Wearable Health Devices
Wearable technology is rapidly evolving, and its integration with telehealth is already underway. Devices such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and health monitors collect continuous health data, enabling real-time monitoring and early intervention. This trend is set to grow, offering more precise and personalized care.
Additionally, as wearable devices become more affordable and user-friendly, their adoption will likely increase, further boosting the effectiveness of Digital Health Technologies.
5.3 Enhanced Remote Care Platforms
Future remote care platforms will be more sophisticated, integrating video consultations, AI-driven diagnostics, and comprehensive patient management systems. These platforms will provide seamless, end-to-end healthcare solutions that are not only efficient but also highly personalized.
In addition, advancements in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) could play a role in training healthcare professionals and even in patient rehabilitation programs.
5.4 Policy Evolution and Global Collaboration
As the telehealth industry expands, there will be an increasing need for updated policies and international collaboration. Governments and regulatory bodies must work together to create frameworks that support innovation while ensuring patient safety and data privacy.
Furthermore, global initiatives and partnerships will be essential in standardizing telehealth practices and driving further technological advancements.
6. How to Implement Telehealth Solutions: Practical Steps
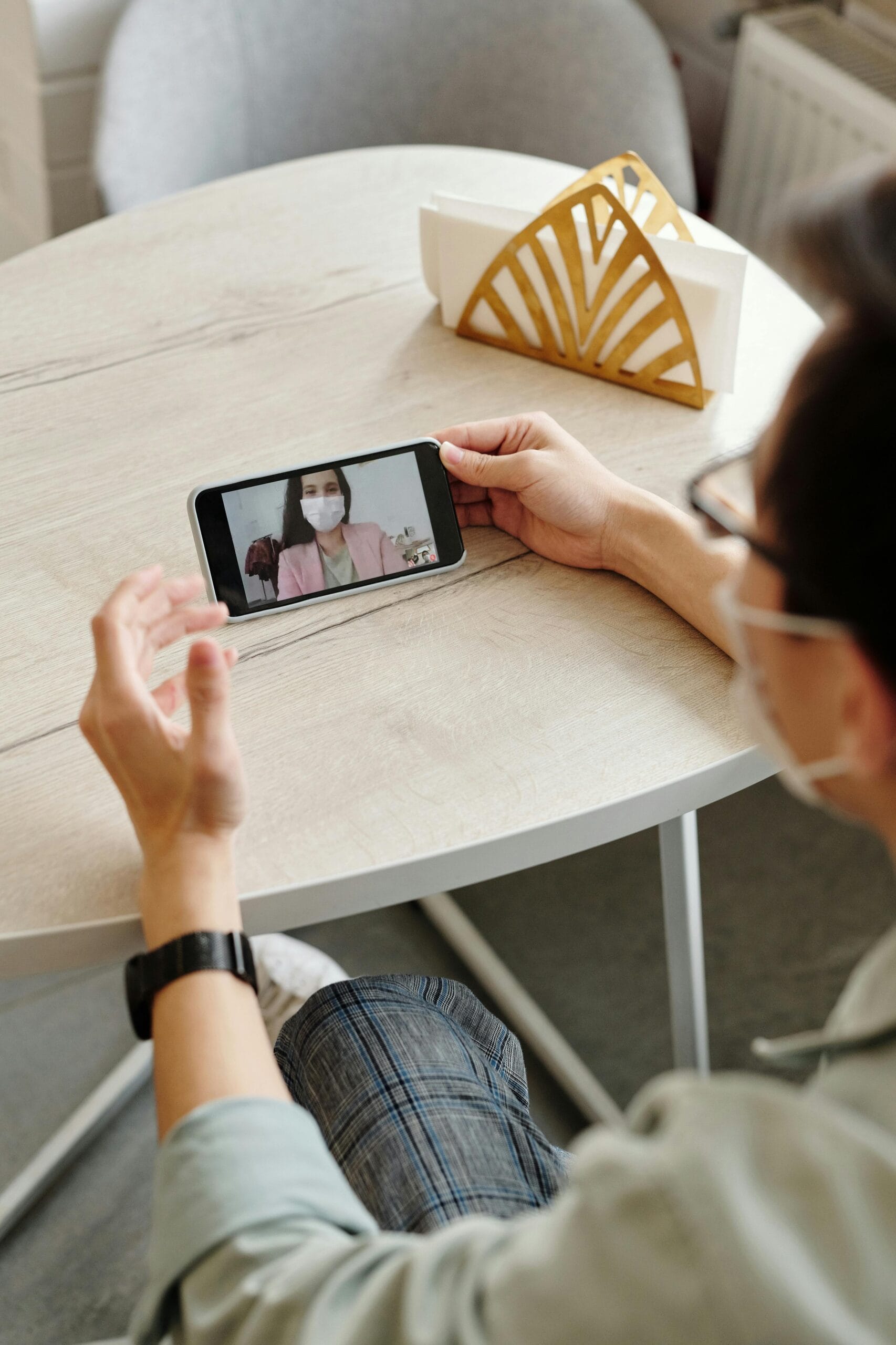

6.1 For Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers looking to integrate telehealth solutions should begin by assessing their current infrastructure and identifying areas for improvement. Implementing a secure, user-friendly telehealth platform is crucial. This includes investing in reliable video conferencing tools, remote monitoring devices, and electronic health record systems.
Moreover, providers should ensure that their staff receives adequate training on using these technologies and maintaining patient privacy. Partnering with technology vendors who specialize in Digital Health Technologies can also help streamline the integration process.
6.2 For Patients
Patients can also take steps to make the most of telehealth services. First, ensure you have a stable internet connection and a compatible device for video consultations. Familiarize yourself with the telehealth platform used by your healthcare provider, and don’t hesitate to ask questions if you’re unsure about any aspect of the service.
Additionally, taking an active role in your healthcare by monitoring your health data through wearable devices can enhance the effectiveness of remote care.
6.3 For Policy Makers
Policy makers play a vital role in the widespread adoption of telehealth solutions. By providing incentives for both providers and patients, updating regulatory frameworks, and promoting digital literacy, governments can accelerate the integration of Digital Health Technologies in everyday healthcare.
Furthermore, policies that encourage innovation and investment in renewable healthcare technologies will be crucial for creating a sustainable healthcare system.
7. Real-World Case Studies and Success Stories
7.1 Case Study: A Community’s Solar-Powered Telehealth Initiative
In one inspiring example, a rural community implemented a telehealth system powered entirely by solar energy. Homeowners and local clinics installed solar panels, reducing energy costs while ensuring continuous access to remote healthcare services. This initiative not only improved health outcomes but also fostered a strong sense of community and sustainability.
7.2 Case Study: A Leading Hospital’s Digital Transformation
A prominent hospital network integrated comprehensive telehealth services into its patient care model. By leveraging advanced video consultation tools, remote patient monitoring devices, and AI-driven diagnostics, the hospital was able to reduce wait times, lower costs, and improve overall patient satisfaction. This transformation has set a benchmark for how Digital Health Technologies can reshape healthcare delivery.
7.3 Success Story: Empowering Patients with Wearable Health Devices
Several healthcare providers have adopted wearable health devices to enable continuous patient monitoring. In one notable success story, a clinic used smartwatches and fitness trackers to monitor patients with chronic conditions. The data collected enabled early intervention, reducing emergency visits and improving patient outcomes. This example highlights how integrating wearables with telehealth can lead to significant improvements in patient care.
8. Conclusion
The future of healthcare lies in the seamless integration of technology and patient care. Digital Health Technologies such as telehealth solutions and remote care are transforming the way we approach healthcare, making it more accessible, efficient, and personalized. As we have explored, these innovations not only reduce healthcare costs and improve outcomes but also empower patients and providers to take control of their health in a rapidly changing world.
By embracing telehealth, investing in cutting-edge digital health solutions, and fostering a collaborative approach between technology providers, healthcare institutions, and policy makers, we can build a more resilient and responsive healthcare system for the future. The journey toward a sustainable and efficient healthcare model is well underway, and every step taken today paves the way for a healthier, more connected tomorrow.
At TechWorldTrends.com, we are dedicated to exploring and sharing the latest trends in Digital Health Technologies. We believe that by staying informed and taking proactive measures, we can revolutionize healthcare and create a better future for everyone.
For more insights on digital health innovations and telehealth solutions, visit our Digital Health Technologies section at TechWorldTrends.com.
